BMI Chart: Understand Your Body Mass Index at a Glance
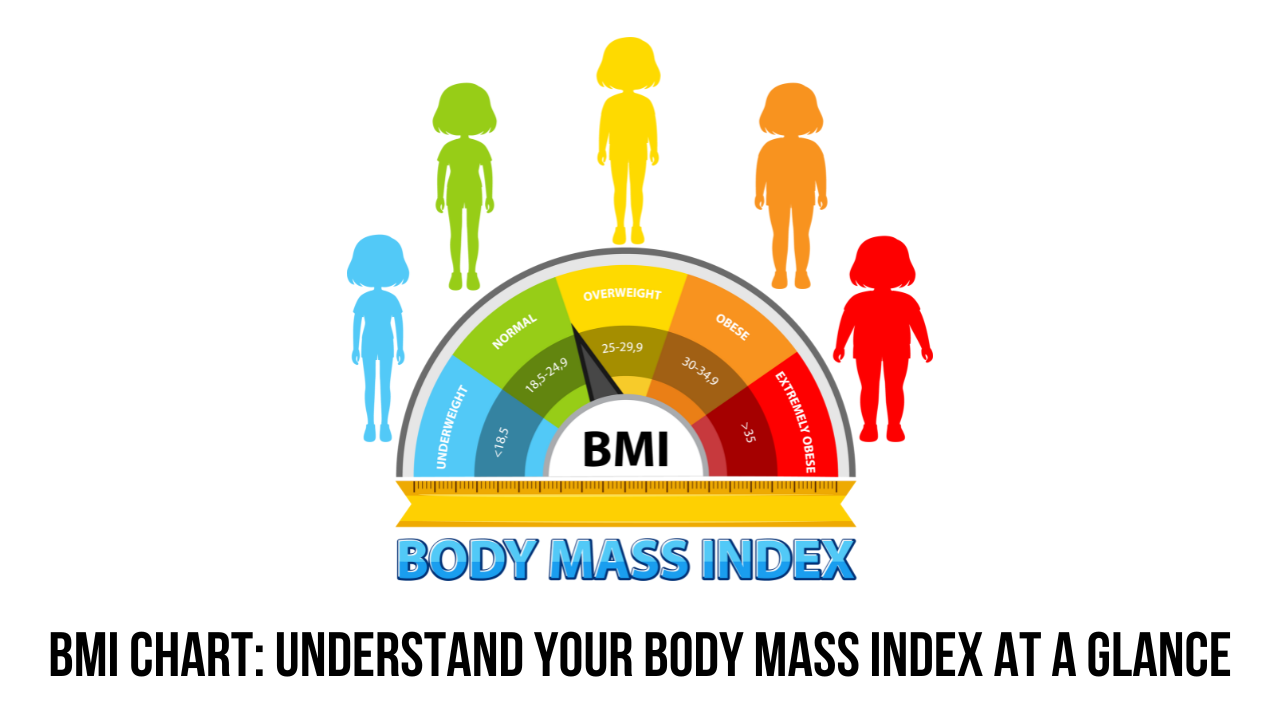
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a simple and commonly used method to assess whether a person’s body weight is appropriate for their height. This tool helps categorize individuals into different weight ranges, giving a general idea of their health based on body fat. Understanding your BMI can give you insights into your physical health and whether you need to make adjustments to your lifestyle.
🧮 What is BMI?
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a screening tool that uses your height and weight to estimate the amount of body fat. It doesn’t directly measure body fat but provides a general overview. The BMI formula is:
BMI=weight(kg)height(m)2BMI = \frac{weight (kg)}{height (m)^2}BMI=height(m)2weight(kg)
This results in a number that places you in a category such as underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese, which can indicate the risk of health issues.
📊 BMI Categories
BMI values fall into different ranges, each corresponding to a weight category. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Underweight: BMI less than 18.5
- Normal weight: BMI between 18.5 and 24.9
- Overweight: BMI between 25 and 29.9
- Obese: BMI 30 or greater
These categories help doctors and health professionals screen for potential weight-related health issues. For example, a higher BMI can indicate a greater risk of developing conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure.
📉 How to Calculate BMI
To calculate your BMI:
- Measure your weight in kilograms.
- Measure your height in meters.
- Use the formula: Weight (kg) ÷ Height² (m²).
Alternatively, you can refer to a BMI chart, which lists the BMI values for different height and weight combinations. BMI charts make it easier to see where you fall without manual calculations.
🩺 Limitations of BMI
Although BMI is widely used, it has limitations. It doesn’t distinguish between muscle and fat, meaning that highly muscular individuals (like athletes) may be classified as overweight or obese, even though they have low body fat. Similarly, BMI doesn’t account for fat distribution, which can influence the risk of health conditions.
Age, gender, and ethnicity also play roles in body fat distribution, which BMI doesn’t consider. Therefore, BMI should be viewed as a guideline, and additional health assessments may be needed to gain a complete understanding of your health.
🏥 Why BMI Matters
Maintaining a healthy BMI is associated with lower risks of chronic conditions, such as:
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Type 2 diabetes
- Certain types of cancer
- Joint problems
Understanding your BMI allows you to take proactive steps toward managing your weight, improving your lifestyle, and reducing your risk of developing these conditions.
How BMI Helps in Weight Loss:
Goal Setting: BMI allows individuals to determine their ideal weight range. By knowing what a healthy BMI looks like, people can set realistic weight loss goals.
Tracking Progress: Regularly checking your BMI as you lose weight helps track progress and keeps motivation high as you see improvements over time.
Risk Assessment: Those with higher BMIs are at greater risk for diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and hypertension. Understanding this can motivate weight loss as a means of reducing these risks[5].
Personalized Plans: BMI is used by healthcare professionals to recommend personalized diet and exercise programs based on a person’s weight category[2].
🌟 Conclusion
The BMI chart provides an easy, accessible tool to quickly assess your body weight relative to your height, offering a general picture of your health. While it has limitations, BMI remains an important part of public health screening tools and personal health management.
To make sure you stay within a healthy range, it’s important to monitor your BMI alongside other health indicators. For personalized advice, consult a healthcare professional who can help assess your individual risk factors beyond BMI.








